What is Dark Data and How Can Enterprises Extract Insights use AI?
Businesses have volumes of data stored in their systems. However, in reality, much of this data is unused data or dark data. Enterprises can extract insights from dark data leveraging AI and gain significantly from it.
Consider a scenario such as e-learning and employee training in an enterprise. Increasingly, such training is delivered through content created in an interoperable format called SCORM (Shareable Interoperable Content Object Reference Model). As the name suggests the idea is to create a course content object that can play well in any enterprise learning management system without any compatibility issues with the user experience.
This interoperability is achieved through a set of common standards between the learning management system and the course content with the help of a programmatic module called SCORM API. The resulting process creates an environment for generating vast amounts of data related to learner activity, learner responses, assessment results, learning behavior, etc. Standards such as xAPI have been specially developed to help capture this data for the purpose of extracting insights related to student activity.
The problem, however, is that such data is rarely used in the right manner or at the right time, resulting in the accumulation of the data in vast amounts in the enterprise LMS data stores and warehouses without ever seeing the light of the day in the form of insight thereby creating a new form of data that is becoming prevalent in several other functional areas as well, called Dark Data.
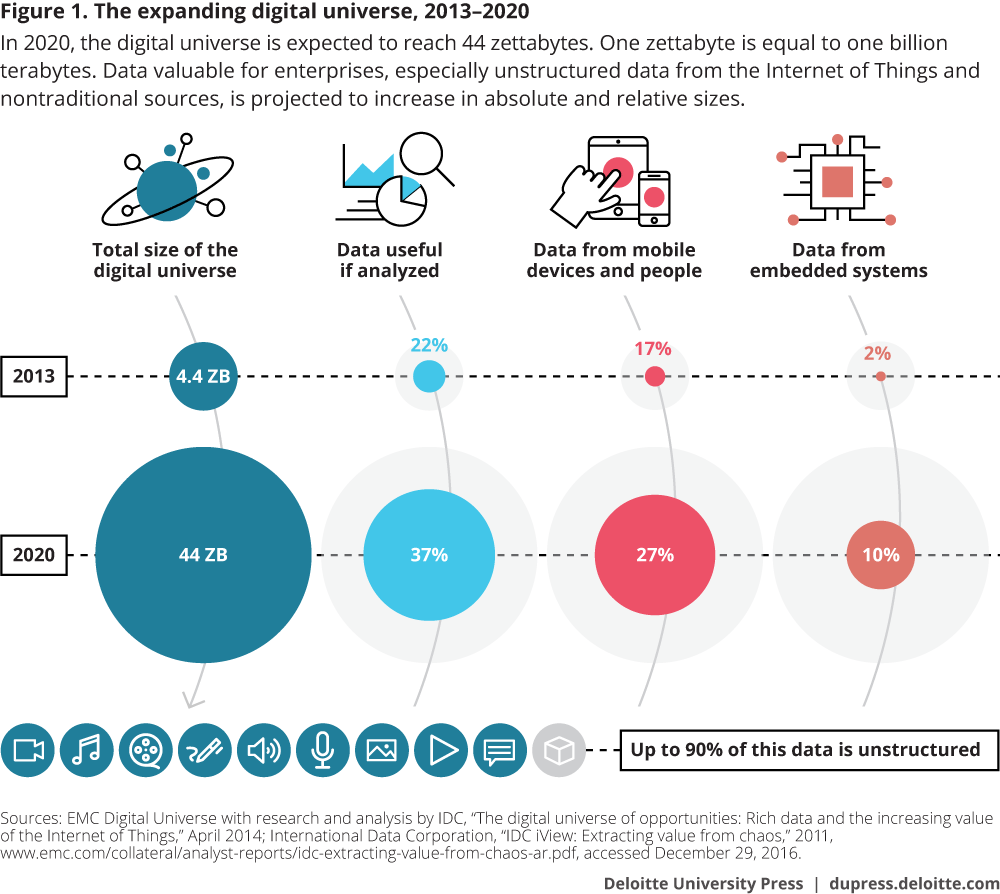
Dark data accounts for 80% of all data generated across enterprises. Dark Data is the type of data that enterprises accumulate during the course of operations but is rarely utilized for any form of processing activity to extract insights. According to Gartner, dark data is “the information assets organizations collect, process, and store during regular business activities, but generally fail to use for other purposes.”
In another example, a CCTV camera installed in a retail store is primarily used for surveillance and monitoring of shopper activity. However, the cameras also capture images that can help extract insights like customer behavior, shelf display and consumption patterns, and customer interests in various products, etc. While the actual process of extracting such complex information from images can be cumbersome, if harnessed, this information can provide valuable insights into store planning and management.
Dark data can take on different forms depending on your industry and the type of business, but common examples include spreadsheets, activity logs, server logs, archived documents, emails, and attachments that are downloaded and then ignored, employee files, survey data, and social media content, etc.
Challenges with Dark Data
Extracting insights from dark data is no mean task. Most dark data typically is in an unstructured format as cited in the examples above. The most complex tasks working with data is extracting a structure from the data to normalize the data points and identifying patterns before extracting any form of insights.
The other challenge with dark data is extracting and establishing data integrity. For example, linking a customer based on activity captured from an image to their retail transaction in a store can be extremely challenging and will require advanced image processing capabilities.
Another more commonly available yet untapped source of data for enterprises is customer support logs. Many enterprises interact with customers and store extraordinary amounts of information collected from them in text and audio format within their systems. Such data is rarely if ever is used in the appropriate amount of time for businesses to extract the insights when they need them.
So what are some of the types of insights that can be extracted from Dark Data? The most common insights that can be extracted are patterns, behaviors, and trends and can be categorized in Real-Time Insights, Operational Insights, Performance Insights, and Strategic Insights. In addition to technical components such as cloud resources, these can also apply to human behaviors and trends such as customers, employees, or other types of users.
These insights also carry a lot of weight when extracted in a timely manner, otherwise, they become “perishable insights”. For example, detecting an anomaly in the behavior of a cloud-based resource is helpful when done at the time of the occurrence of such an event and not after the anomaly has passed. Such timely insight will help the system administrators in controlling and mitigating relevant issues.
How to Unlock Dark Data?
Here are a few things you can do to unlock dark data:
1. Review your existing data inventory
- Organizations must take into account the different types of data from their existing operations and processes.
- Identify data that can help in extracting insights that can be categorized as Real-Time, Operational, Performance, or Strategic.
- Identify and discard stale data that can no longer add any meaningful value to insights.
2. Identify and establish context at the point of data generation
- The most difficult aspect of out of process data is establishing the context in which it was generated, so organizations should take measures to account for all the data generating processes and ensure that appropriate controls are in place to store and tag contextual information such as timestamps, customer information, product information, business unit, etc.
3. Structure and analyze unstructured data
- Leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to perform analysis such as Keyword extraction, Spam detection, Sentiment Analysis, and Intent classification among others.
- Utilize media processing techniques such as speech to text or Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract information from images, videos, and audios and then apply NLP techniques mentioned above to extract similar insights.
4. Optimize processes and reduce dark data
- Finally, audit the processes in the organization to streamline and reduce the areas in which dark data generation and storage are prevalent.
Dark data in your business could be hiding useful insights that can pave the way for innovation, automation, and improved customer satisfaction.
At Qualetics, our proprietary streaming data API can help organizations in capturing data that traditionally might be classified as dark data, with contextual information, and extracting real-time as well as operational, performance, and NLP based insights. Book a demo here to talk to our data experts.


